本节需要用的函数
基本函数(step、sigmoid)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
import numpy as np
def identity_function(x):
return x
def step_function(x):
return np.array(x > 0, dtype=np.int)
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def sigmoid_grad(x):
return (1.0 - sigmoid(x)) * sigmoid(x)
def relu(x):
return np.maximum(0, x)
def relu_grad(x):
grad = np.zeros(x)
grad[x>=0] = 1
return grad
def softmax(x):
if x.ndim == 2:
x = x.T
x = x - np.max(x, axis=0)
y = np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x), axis=0)
return y.T
x = x - np.max(x) # 溢出对策
return np.exp(x) / np.sum(np.exp(x))
def mean_squared_error(y, t):
return 0.5 * np.sum((y-t)**2)
def cross_entropy_error(y, t):
if y.ndim == 1:
t = t.reshape(1, t.size)
y = y.reshape(1, y.size)
# 监督数据是one-hot-vector的情况下,转换为正确解标签的索引
if t.size == y.size:
t = t.argmax(axis=1)
batch_size = y.shape[0]
return -np.sum(np.log(y[np.arange(batch_size), t] + 1e-7)) / batch_size
def softmax_loss(X, t):
y = softmax(X)
return cross_entropy_error(y, t)
数值微分
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
def _numerical_gradient_1d(f, x):
h = 1e-4 # 0.0001
grad = np.zeros_like(x)
for idx in range(x.size):
tmp_val = x[idx]
x[idx] = float(tmp_val) + h
fxh1 = f(x) # f(x+h)
x[idx] = tmp_val - h
fxh2 = f(x) # f(x-h)
grad[idx] = (fxh1 - fxh2) / (2*h)
x[idx] = tmp_val # 还原值
return grad
def numerical_gradient_2d(f, X):
if X.ndim == 1:
return _numerical_gradient_1d(f, X)
else:
grad = np.zeros_like(X)
for idx, x in enumerate(X):
grad[idx] = _numerical_gradient_1d(f, x)
return grad
def numerical_gradient(f, x):
h = 1e-4 # 0.0001
grad = np.zeros_like(x)
it = np.nditer(x, flags=['multi_index'], op_flags=['readwrite'])
while not it.finished:
idx = it.multi_index
tmp_val = x[idx]
x[idx] = float(tmp_val) + h
fxh1 = f(x) # f(x+h)
x[idx] = tmp_val - h
fxh2 = f(x) # f(x-h)
grad[idx] = (fxh1 - fxh2) / (2*h)
x[idx] = tmp_val # 还原值
it.iternext()
return grad
基本层(ReLU、Sigmoid)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
class Relu:
def __init__(self):
self.mask = None
def forward(self, x):
self.mask = (x <= 0)
out = x.copy()
out[self.mask] = 0
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dout[self.mask] = 0
dx = dout
return dx
class Sigmoid:
def __init__(self):
self.out = None
def forward(self, x):
out = sigmoid(x)
self.out = out
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dx = dout * (1.0 - self.out) * self.out
return dx
class Affine:
def __init__(self, W, b):
self.W =W
self.b = b
self.x = None
self.original_x_shape = None
# 权重和偏置参数的导数
self.dW = None
self.db = None
def forward(self, x):
# 对应张量
self.original_x_shape = x.shape
x = x.reshape(x.shape[0], -1)
self.x = x
out = np.dot(self.x, self.W) + self.b
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dx = np.dot(dout, self.W.T)
self.dW = np.dot(self.x.T, dout)
self.db = np.sum(dout, axis=0)
dx = dx.reshape(*self.original_x_shape) # 还原输入数据的形状(对应张量)
return dx
class SoftmaxWithLoss:
def __init__(self):
self.loss = None
self.y = None # softmax的输出
self.t = None # 监督数据
def forward(self, x, t):
self.t = t
self.y = softmax(x)
self.loss = cross_entropy_error(self.y, self.t)
return self.loss
def backward(self, dout=1):
batch_size = self.t.shape[0]
if self.t.size == self.y.size: # 监督数据是one-hot-vector的情况
dx = (self.y - self.t) / batch_size
else:
dx = self.y.copy()
dx[np.arange(batch_size), self.t] -= 1
dx = dx / batch_size
return dx
class Dropout:
"""
http://arxiv.org/abs/1207.0580
"""
def __init__(self, dropout_ratio=0.5):
self.dropout_ratio = dropout_ratio
self.mask = None
def forward(self, x, train_flg=True):
if train_flg:
self.mask = np.random.rand(*x.shape) > self.dropout_ratio
return x * self.mask
else:
return x * (1.0 - self.dropout_ratio)
def backward(self, dout):
return dout * self.mask
class BatchNormalization:
"""
http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03167
"""
def __init__(self, gamma, beta, momentum=0.9, running_mean=None, running_var=None):
self.gamma = gamma
self.beta = beta
self.momentum = momentum
self.input_shape = None # Conv层的情况下为4维,全连接层的情况下为2维
# 测试时使用的平均值和方差
self.running_mean = running_mean
self.running_var = running_var
# backward时使用的中间数据
self.batch_size = None
self.xc = None
self.std = None
self.dgamma = None
self.dbeta = None
def forward(self, x, train_flg=True):
self.input_shape = x.shape
if x.ndim != 2:
N, C, H, W = x.shape
x = x.reshape(N, -1)
out = self.__forward(x, train_flg)
return out.reshape(*self.input_shape)
def __forward(self, x, train_flg):
if self.running_mean is None:
N, D = x.shape
self.running_mean = np.zeros(D)
self.running_var = np.zeros(D)
if train_flg:
mu = x.mean(axis=0)
xc = x - mu
var = np.mean(xc**2, axis=0)
std = np.sqrt(var + 10e-7)
xn = xc / std
self.batch_size = x.shape[0]
self.xc = xc
self.xn = xn
self.std = std
self.running_mean = self.momentum * self.running_mean + (1-self.momentum) * mu
self.running_var = self.momentum * self.running_var + (1-self.momentum) * var
else:
xc = x - self.running_mean
xn = xc / ((np.sqrt(self.running_var + 10e-7)))
out = self.gamma * xn + self.beta
return out
def backward(self, dout):
if dout.ndim != 2:
N, C, H, W = dout.shape
dout = dout.reshape(N, -1)
dx = self.__backward(dout)
dx = dx.reshape(*self.input_shape)
return dx
def __backward(self, dout):
dbeta = dout.sum(axis=0)
dgamma = np.sum(self.xn * dout, axis=0)
dxn = self.gamma * dout
dxc = dxn / self.std
dstd = -np.sum((dxn * self.xc) / (self.std * self.std), axis=0)
dvar = 0.5 * dstd / self.std
dxc += (2.0 / self.batch_size) * self.xc * dvar
dmu = np.sum(dxc, axis=0)
dx = dxc - dmu / self.batch_size
self.dgamma = dgamma
self.dbeta = dbeta
return dx
下载MNIST
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
try:
import urllib.request
except ImportError:
raise ImportError('You should use Python 3.x')
import os.path
from IPython.terminal.embed import InteractiveShellEmbed
import gzip
import pickle
import os
import numpy as np
url_base = 'http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/'
key_file = {
'train_img':'train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz',
'train_label':'train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz',
'test_img':'t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz',
'test_label':'t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz'
}
## if you run in terminal, run this
# dataset_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
## if you run in IPython, run this
ip_shell = InteractiveShellEmbed()
dataset_dir = ip_shell.magic("%pwd")
save_file = dataset_dir + "/mnist.pkl"
train_num = 60000
test_num = 10000
img_dim = (1, 28, 28)
img_size = 784
def _download(file_name):
file_path = dataset_dir + "/" + file_name
if os.path.exists(file_path):
return
print("Downloading " + file_name + " ... ")
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url_base + file_name, file_path)
print("Done")
def download_mnist():
for v in key_file.values():
_download(v)
def _load_label(file_name):
file_path = dataset_dir + "/" + file_name
print("Converting " + file_name + " to NumPy Array ...")
with gzip.open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
labels = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=8)
print("Done")
return labels
def _load_img(file_name):
file_path = dataset_dir + "/" + file_name
print("Converting " + file_name + " to NumPy Array ...")
with gzip.open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
data = np.frombuffer(f.read(), np.uint8, offset=16)
data = data.reshape(-1, img_size)
print("Done")
return data
def _convert_numpy():
dataset = {}
dataset['train_img'] = _load_img(key_file['train_img'])
dataset['train_label'] = _load_label(key_file['train_label'])
dataset['test_img'] = _load_img(key_file['test_img'])
dataset['test_label'] = _load_label(key_file['test_label'])
return dataset
def init_mnist():
download_mnist()
dataset = _convert_numpy()
print("Creating pickle file ...")
with open(save_file, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(dataset, f, -1)
print("Done!")
def _change_one_hot_label(X):
T = np.zeros((X.size, 10))
for idx, row in enumerate(T):
row[X[idx]] = 1
return T
def load_mnist(normalize=True, flatten=True, one_hot_label=False):
"""读入MNIST数据集
Parameters
----------
normalize : 将图像的像素值正规化为0.0~1.0
one_hot_label :
one_hot_label为True的情况下,标签作为one-hot数组返回
one-hot数组是指[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]这样的数组
flatten : 是否将图像展开为一维数组
Returns
-------
(训练图像, 训练标签), (测试图像, 测试标签)
"""
if not os.path.exists(save_file):
init_mnist()
with open(save_file, 'rb') as f:
dataset = pickle.load(f)
if normalize:
for key in ('train_img', 'test_img'):
dataset[key] = dataset[key].astype(np.float32)
dataset[key] /= 255.0
if one_hot_label:
dataset['train_label'] = _change_one_hot_label(dataset['train_label'])
dataset['test_label'] = _change_one_hot_label(dataset['test_label'])
if not flatten:
for key in ('train_img', 'test_img'):
dataset[key] = dataset[key].reshape(-1, 1, 28, 28)
return (dataset['train_img'], dataset['train_label']), (dataset['test_img'], dataset['test_label'])
if __name__ == '__main__':
init_mnist()
SGD
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
import numpy as np
class SGD:
"""随机梯度下降法(Stochastic Gradient Descent)"""
def __init__(self, lr=0.01):
self.lr = lr
def update(self, params, grads):
for key in params.keys():
params[key] -= self.lr * grads[key]
class Momentum:
"""Momentum SGD"""
def __init__(self, lr=0.01, momentum=0.9):
self.lr = lr
self.momentum = momentum
self.v = None
def update(self, params, grads):
if self.v is None:
self.v = {}
for key, val in params.items():
self.v[key] = np.zeros_like(val)
for key in params.keys():
self.v[key] = self.momentum*self.v[key] - self.lr*grads[key]
params[key] += self.v[key]
class Nesterov:
"""Nesterov's Accelerated Gradient (http://arxiv.org/abs/1212.0901)"""
def __init__(self, lr=0.01, momentum=0.9):
self.lr = lr
self.momentum = momentum
self.v = None
def update(self, params, grads):
if self.v is None:
self.v = {}
for key, val in params.items():
self.v[key] = np.zeros_like(val)
for key in params.keys():
self.v[key] *= self.momentum
self.v[key] -= self.lr * grads[key]
params[key] += self.momentum * self.momentum * self.v[key]
params[key] -= (1 + self.momentum) * self.lr * grads[key]
class AdaGrad:
"""AdaGrad"""
def __init__(self, lr=0.01):
self.lr = lr
self.h = None
def update(self, params, grads):
if self.h is None:
self.h = {}
for key, val in params.items():
self.h[key] = np.zeros_like(val)
for key in params.keys():
self.h[key] += grads[key] * grads[key]
params[key] -= self.lr * grads[key] / (np.sqrt(self.h[key]) + 1e-7)
class RMSprop:
"""RMSprop"""
def __init__(self, lr=0.01, decay_rate = 0.99):
self.lr = lr
self.decay_rate = decay_rate
self.h = None
def update(self, params, grads):
if self.h is None:
self.h = {}
for key, val in params.items():
self.h[key] = np.zeros_like(val)
for key in params.keys():
self.h[key] *= self.decay_rate
self.h[key] += (1 - self.decay_rate) * grads[key] * grads[key]
params[key] -= self.lr * grads[key] / (np.sqrt(self.h[key]) + 1e-7)
class Adam:
"""Adam (http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980v8)"""
def __init__(self, lr=0.001, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.999):
self.lr = lr
self.beta1 = beta1
self.beta2 = beta2
self.iter = 0
self.m = None
self.v = None
def update(self, params, grads):
if self.m is None:
self.m, self.v = {}, {}
for key, val in params.items():
self.m[key] = np.zeros_like(val)
self.v[key] = np.zeros_like(val)
self.iter += 1
lr_t = self.lr * np.sqrt(1.0 - self.beta2**self.iter) / (1.0 - self.beta1**self.iter)
for key in params.keys():
#self.m[key] = self.beta1*self.m[key] + (1-self.beta1)*grads[key]
#self.v[key] = self.beta2*self.v[key] + (1-self.beta2)*(grads[key]**2)
self.m[key] += (1 - self.beta1) * (grads[key] - self.m[key])
self.v[key] += (1 - self.beta2) * (grads[key]**2 - self.v[key])
params[key] -= lr_t * self.m[key] / (np.sqrt(self.v[key]) + 1e-7)
#unbias_m += (1 - self.beta1) * (grads[key] - self.m[key]) # correct bias
#unbisa_b += (1 - self.beta2) * (grads[key]*grads[key] - self.v[key]) # correct bias
#params[key] += self.lr * unbias_m / (np.sqrt(unbisa_b) + 1e-7)
训练器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
import numpy as np
class Trainer:
"""进行神经网络的训练的类
"""
def __init__(self, network, x_train, t_train, x_test, t_test,
epochs=20, mini_batch_size=100,
optimizer='SGD', optimizer_param={'lr':0.01},
evaluate_sample_num_per_epoch=None, verbose=True):
self.network = network
self.verbose = verbose
self.x_train = x_train
self.t_train = t_train
self.x_test = x_test
self.t_test = t_test
self.epochs = epochs
self.batch_size = mini_batch_size
self.evaluate_sample_num_per_epoch = evaluate_sample_num_per_epoch
# optimzer
optimizer_class_dict = {'sgd':SGD, 'momentum':Momentum, 'nesterov':Nesterov,
'adagrad':AdaGrad, 'rmsprpo':RMSprop, 'adam':Adam}
self.optimizer = optimizer_class_dict[optimizer.lower()](**optimizer_param)
self.train_size = x_train.shape[0]
self.iter_per_epoch = max(self.train_size / mini_batch_size, 1)
self.max_iter = int(epochs * self.iter_per_epoch)
self.current_iter = 0
self.current_epoch = 0
self.train_loss_list = []
self.train_acc_list = []
self.test_acc_list = []
def train_step(self):
batch_mask = np.random.choice(self.train_size, self.batch_size)
x_batch = self.x_train[batch_mask]
t_batch = self.t_train[batch_mask]
grads = self.network.gradient(x_batch, t_batch)
self.optimizer.update(self.network.params, grads)
loss = self.network.loss(x_batch, t_batch)
self.train_loss_list.append(loss)
if self.verbose: print("train loss:" + str(loss))
if self.current_iter % self.iter_per_epoch == 0:
self.current_epoch += 1
x_train_sample, t_train_sample = self.x_train, self.t_train
x_test_sample, t_test_sample = self.x_test, self.t_test
if not self.evaluate_sample_num_per_epoch is None:
t = self.evaluate_sample_num_per_epoch
x_train_sample, t_train_sample = self.x_train[:t], self.t_train[:t]
x_test_sample, t_test_sample = self.x_test[:t], self.t_test[:t]
train_acc = self.network.accuracy(x_train_sample, t_train_sample)
test_acc = self.network.accuracy(x_test_sample, t_test_sample)
self.train_acc_list.append(train_acc)
self.test_acc_list.append(test_acc)
if self.verbose: print("=== epoch:" + str(self.current_epoch) + ", train acc:" + str(train_acc) + ", test acc:" + str(test_acc) + " ===")
self.current_iter += 1
def train(self):
for i in range(self.max_iter):
self.train_step()
test_acc = self.network.accuracy(self.x_test, self.t_test)
if self.verbose:
print("=============== Final Test Accuracy ===============")
print("test acc:" + str(test_acc))
卷积神经网络
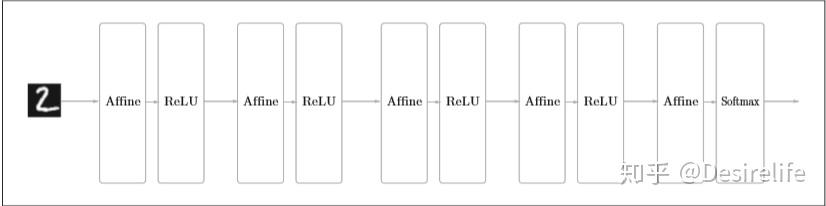
卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Newtwork,CNN) 与之前介绍的神经网络的不同之处在于,之前的神经网络的所有神经元之间都有连接,称为 全连接(fully-connected),这是通过 Affine层(全连接层)实现的。比如下面的一个神经网络:
卷积网络中,增加了 Convolution层(卷积层) 和 Pooling层(池化层),将之前的 Affine-ReLU 改成了 Convolution-ReLU-Pooling
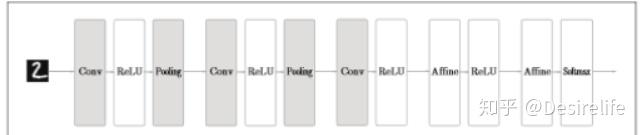
下面来介绍新增的这两个层。
卷积层
全连接层有个很大的问题,就是无论数据是几维的,都会拉平成一维数据。比如之前的MNIST数据集,本来是 $28\times 28$ 的图像,输入时却成了 $784\times 1$ 的数组。因此,图像中的很多空间信息都损失了。而卷积层则可以接受图像输入,并输出图像,我们将输入输出的数据称为 特征图(feature map)。
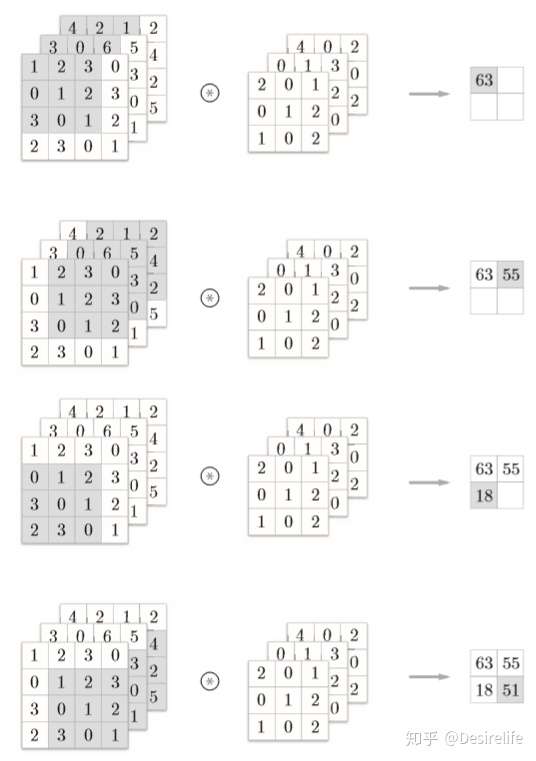
卷积层主要做的是卷积运算,运算过程如下:用一个 滤波器 对图像进行扫描,将图像的被扫部分与滤波器进行元素相乘再求和,从而得到结果中的一个子像素。
\[\newcommand{\blue}[1]{\color{Cyan}#1} \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 2 & 3\\ 3 & 0 & 1 & 2\\ 2 & 3 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} * \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 1 & 2\\ 1 & 0 & 2 \end{bmatrix} =\begin{bmatrix} 15 & 16\\ 6 & 15 \end{bmatrix} \\ \begin{bmatrix} 15 & \\ & \end{bmatrix} =\begin{bmatrix} \blue{1} & \blue2 & \blue3 & 0\\ \blue0 & \blue1 & \blue2 & 3\\ \blue3 & \blue0 & \blue1 & 2\\ 2 & 3 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \odot \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 1 & 2\\ 1 & 0 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \\ \begin{bmatrix} & 16 \\ & \end{bmatrix} =\begin{bmatrix} 1 & \blue2 & \blue3 & \blue0\\ 0 & \blue1 & \blue2 & \blue3\\ 3 & \blue0 & \blue1 & \blue2\\ 2 & 3 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \odot \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 1 & 2\\ 1 & 0 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \\ \begin{bmatrix} & \\ 6 & \end{bmatrix} =\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3 & 0\\ \blue0 & \blue1 & \blue2 & 3\\ \blue3 & \blue0 & \blue1 & 2\\ \blue2 & \blue3 & \blue0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \odot \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 1 & 2\\ 1 & 0 & 2 \end{bmatrix} \\ \begin{bmatrix} & \\ & 15 \end{bmatrix} =\begin{bmatrix} 1 & 2 & 3 & 0\\ 0 & \blue1 & \blue2 & \blue3\\ 3 & \blue0 & \blue1 & \blue2\\ 2 & \blue3 & \blue0 & \blue1 \end{bmatrix} \odot \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 1 & 2\\ 1 & 0 & 2 \end{bmatrix}\]卷积层中也有偏置,偏置一般就是一个数字,加到卷积结果的所有元素上。这里就不附图了。
注意到上面 $4\times 4$ 矩阵经过卷积后变成了 $2\times 2$ 矩阵,说明卷积会缩小图像。如果经过多次卷积,那么图像最终会缩成 $1\times 1$。为了使得图像大小不改变,我们会对输入数据进行 填充(padding),就是在边上加一圈 0,这样卷积完还是一样大:
\[\newcommand{\grey}[1]{\color{Grey}#1} \begin{bmatrix} \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0\\ \grey0 & 1 & 2 & 3 & 0 & \grey0\\ \grey0 & 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 & \grey0\\ \grey0 & 3 & 0 & 1 & 2 & \grey0\\ \grey0 & 2 & 3 & 0 & 1 & \grey0\\ \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0 \end{bmatrix} * \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 1 & 2\\ 1 & 0 & 2 \end{bmatrix} =\begin{bmatrix} 7 & 12 & 10 & 2\\ 4 & 15 & 16 & 10\\ 10 & 6 & 15 & 6\\ 8 & 10 & 4 & 3 \end{bmatrix}\]此外,还有一个重要参数就是 步幅(stride),即每次滤波器上下左右移动的距离。前面的步幅是 1,我们也可以改成 3:
\[\newcommand{\grey}[1]{\color{Grey}#1} \begin{bmatrix} \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0\\ \grey0 & 1 & 2 & 3 & 0 & \grey0\\ \grey0 & 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 & \grey0\\ \grey0 & 3 & 0 & 1 & 2 & \grey0\\ \grey0 & 2 & 3 & 0 & 1 & \grey0\\ \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0 & \grey0 \end{bmatrix} * \begin{bmatrix} 2 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 1 & 2\\ 1 & 0 & 2 \end{bmatrix} =\begin{bmatrix} 7 & 2\\ 8 & 3 \end{bmatrix}\]假设输入大小为 $(H,W)$,滤波器大小为 $(FH,FW)$,填充为 $P$,步幅为 $S$,那么输出大小 $(OH,OW)$ 满足:
\[OH = \frac{H+2P-FH}{S}+1\\ OW = \frac{W+2P-FW}{S}+1\]如果除不尽的话,可以报错,也可以四舍五入。
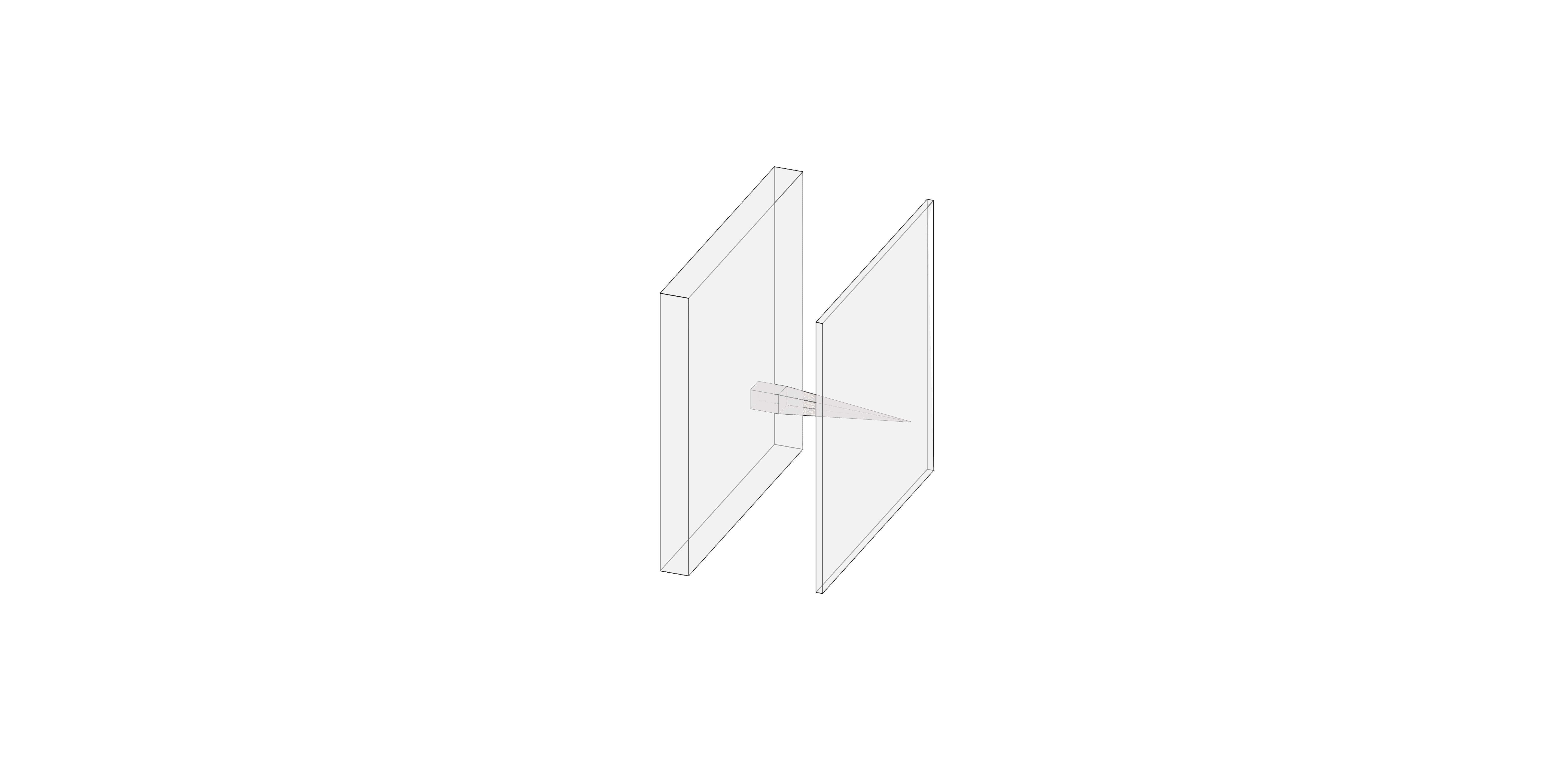
对于高维数据,可以用高维滤波器进行卷积。下图展示了一个三维数据经过三维滤波器卷积后,得到了一个一维数据。
或者也可以用多个的滤波器进行卷积,这样会得到一个多维的数据:
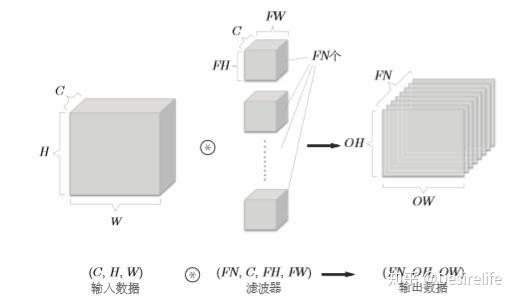
对于有多个通道的图像(3维数据),我们一般按照(channel, height, width)的顺序写,滤波器也同理。我们可以用一个方块的厚度、长、宽来表示,如下图(或上图):
卷积同样可以进行批处理,此时一个batch的数据写成(batch_size, channel, height, width)
池化层
池化层与卷积层类似,但它并不是相乘再求和,而是取最大值(Max池化)或平均值(Average池化)。比如:
\[\newcommand{\blue}[1]{\color{Cyan}#1} \newcommand{\red}[1]{\color{Magenta}#1} \newcommand{\orange}[1]{\color{Orange}#1} \newcommand{\green}[1]{\color{Lime}#1} \begin{bmatrix} \blue1 & \blue2 & \red3 & \red0\\ \blue0 & \blue1 & \red2 & \red3\\ \orange3 & \orange0 & \green1 & \green2\\ \orange2 & \orange3 & \green0 & \green1 \end{bmatrix} \Rightarrow \begin{bmatrix} \blue2 & \red3\\ \orange4 & \green5 \end{bmatrix}\]一般来说,池化的窗口大小与步幅会设定成相同的值。池化层与卷积的不同之处在于:
- 池化层没有要学习的参数,只是取最大或平均值
- 数据经过池化层后通道数不发生变换,各通道是独立进行的
- 池化层对微小的变化具有鲁棒性(这样图像就算有微小的位移也不会造成影响)
卷积层的实现
如果使用循环来实现卷积,那么就会十分复杂且速度很慢。这里我们利用 im2col 来实现。im2col 会将图像中每个滤波区域横向转化成一列(我也不知道为什么不说“转化为一行”),将滤波器纵向转化成一列,这样,就可以通过矩阵相乘一次性得到卷积结果,然后再 reshape 为输出数据的大小。
im2col
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
import numpy as np
def conv_output_size(input_size, filter_size, stride=1, pad=0):
return (input_size + 2*pad - filter_size) / stride + 1
def im2col(input_data, filter_h, filter_w, stride=1, pad=0):
"""
Parameters
----------
input_data : 由(数据量, 通道, 高, 长)的4维数组构成的输入数据
filter_h : 滤波器的高
filter_w : 滤波器的长
stride : 步幅
pad : 填充
Returns
-------
col : 2维数组
"""
N, C, H, W = input_data.shape #获取数据的形状
out_h = (H + 2*pad - filter_h)//stride + 1 #输出数据的高度
out_w = (W + 2*pad - filter_w)//stride + 1 #输出数据的宽度
img = np.pad(input_data, [(0,0), (0,0), (pad, pad), (pad, pad)], 'constant') #填充
col = np.zeros((N, C, filter_h, filter_w, out_h, out_w))
for y in range(filter_h):
y_max = y + stride*out_h
for x in range(filter_w):
x_max = x + stride*out_w
col[:, :, y, x, :, :] = img[:, :, y:y_max:stride, x:x_max:stride]
col = col.transpose(0, 4, 5, 1, 2, 3).reshape(N*out_h*out_w, -1)
return col
def col2im(col, input_shape, filter_h, filter_w, stride=1, pad=0):
"""
Parameters
----------
col :
input_shape : 输入数据的形状(例:(10, 1, 28, 28))
filter_h :
filter_w
stride
pad
Returns
-------
"""
N, C, H, W = input_shape
out_h = (H + 2*pad - filter_h)//stride + 1
out_w = (W + 2*pad - filter_w)//stride + 1
col = col.reshape(N, out_h, out_w, C, filter_h, filter_w).transpose(0, 3, 4, 5, 1, 2)
img = np.zeros((N, C, H + 2*pad + stride - 1, W + 2*pad + stride - 1))
for y in range(filter_h):
y_max = y + stride*out_h
for x in range(filter_w):
x_max = x + stride*out_w
img[:, :, y:y_max:stride, x:x_max:stride] += col[:, :, y, x, :, :]
return img[:, :, pad:H + pad, pad:W + pad]
x = np.random.rand(1,3,7,7)
col1 = im2col(x,5,5,stride=1,pad=0)
print(col1.shape)
OUTPUT:
(9, 75)
经过 im2col 后,卷积和Affine十分相似,其反向传播的过程也是类似的。实现方法如下:
class Convolution:
def __init__(self, W, b, stride=1, pad=0):
self.W = W
self.b = b
self.stride = stride
self.pad = pad
# 中间数据(backward时使用)
self.x = None
self.col = None
self.col_W = None
# 权重和偏置参数的梯度
self.dW = None
self.db = None
def forward(self, x):
FN, C, FH, FW = self.W.shape
N, C, H, W = x.shape
out_h = 1 + int((H + 2*self.pad - FH) / self.stride)
out_w = 1 + int((W + 2*self.pad - FW) / self.stride)
col = im2col(x, FH, FW, self.stride, self.pad)
col_W = self.W.reshape(FN, -1).T
out = np.dot(col, col_W) + self.b
out = out.reshape(N, out_h, out_w, -1).transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
self.x = x
self.col = col
self.col_W = col_W
return out
def backward(self, dout):
FN, C, FH, FW = self.W.shape
dout = dout.transpose(0,2,3,1).reshape(-1, FN)
self.db = np.sum(dout, axis=0)
self.dW = np.dot(self.col.T, dout)
self.dW = self.dW.transpose(1, 0).reshape(FN, C, FH, FW)
dcol = np.dot(dout, self.col_W.T)
dx = col2im(dcol, self.x.shape, FH, FW, self.stride, self.pad)
return dx
池化层的实现
池化层也是利用 im2col 来实现。
class Pooling:
def __init__(self, pool_h, pool_w, stride=1, pad=0):
self.pool_h = pool_h
self.pool_w = pool_w
self.stride = stride
self.pad = pad
self.x = None
self.arg_max = None
def forward(self, x):
N, C, H, W = x.shape
out_h = int(1 + (H - self.pool_h) / self.stride)
out_w = int(1 + (W - self.pool_w) / self.stride)
col = im2col(x, self.pool_h, self.pool_w, self.stride, self.pad)
col = col.reshape(-1, self.pool_h*self.pool_w)
arg_max = np.argmax(col, axis=1)
out = np.max(col, axis=1)
out = out.reshape(N, out_h, out_w, C).transpose(0, 3, 1, 2)
self.x = x
self.arg_max = arg_max
return out
def backward(self, dout):
dout = dout.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
pool_size = self.pool_h * self.pool_w
dmax = np.zeros((dout.size, pool_size))
dmax[np.arange(self.arg_max.size), self.arg_max.flatten()] = dout.flatten()
dmax = dmax.reshape(dout.shape + (pool_size,))
dcol = dmax.reshape(dmax.shape[0] * dmax.shape[1] * dmax.shape[2], -1)
dx = col2im(dcol, self.x.shape, self.pool_h, self.pool_w, self.stride, self.pad)
return dx
构建CNN
下面我们来构建一个简单的CNN网络用于识别 MNIST,其构成为:
- Conv
- ReLU
- Pooling
- Affine
- ReLU
- Affine
- Softmax
import pickle
import numpy as np
from collections import OrderedDict
class SimpleConvNet:
"""简单的ConvNet
conv - relu - pool - affine - relu - affine - softmax
Parameters
----------
input_size : 输入大小(MNIST的情况下为784)
hidden_size_list : 隐藏层的神经元数量的列表(e.g. [100, 100, 100])
output_size : 输出大小(MNIST的情况下为10)
activation : 'relu' or 'sigmoid'
weight_init_std : 指定权重的标准差(e.g. 0.01)
指定'relu'或'he'的情况下设定“He的初始值”
指定'sigmoid'或'xavier'的情况下设定“Xavier的初始值”
"""
def __init__(self, input_dim=(1, 28, 28),
conv_param={'filter_num':30, 'filter_size':5, 'pad':0, 'stride':1},
hidden_size=100, output_size=10, weight_init_std=0.01):
filter_num = conv_param['filter_num']
filter_size = conv_param['filter_size']
filter_pad = conv_param['pad']
filter_stride = conv_param['stride']
input_size = input_dim[1]
conv_output_size = (input_size - filter_size + 2*filter_pad) / filter_stride + 1
pool_output_size = int(filter_num * (conv_output_size/2) * (conv_output_size/2))
# 初始化权重
self.params = {}
self.params['W1'] = weight_init_std * \
np.random.randn(filter_num, input_dim[0], filter_size, filter_size)
self.params['b1'] = np.zeros(filter_num)
self.params['W2'] = weight_init_std * \
np.random.randn(pool_output_size, hidden_size)
self.params['b2'] = np.zeros(hidden_size)
self.params['W3'] = weight_init_std * \
np.random.randn(hidden_size, output_size)
self.params['b3'] = np.zeros(output_size)
# 生成层
self.layers = OrderedDict()
self.layers['Conv1'] = Convolution(self.params['W1'], self.params['b1'],
conv_param['stride'], conv_param['pad'])
self.layers['Relu1'] = Relu()
self.layers['Pool1'] = Pooling(pool_h=2, pool_w=2, stride=2)
self.layers['Affine1'] = Affine(self.params['W2'], self.params['b2'])
self.layers['Relu2'] = Relu()
self.layers['Affine2'] = Affine(self.params['W3'], self.params['b3'])
self.last_layer = SoftmaxWithLoss()
def predict(self, x):
for layer in self.layers.values():
x = layer.forward(x)
return x
def loss(self, x, t):
"""求损失函数
参数x是输入数据、t是教师标签
"""
y = self.predict(x)
return self.last_layer.forward(y, t)
def accuracy(self, x, t, batch_size=100):
if t.ndim != 1 : t = np.argmax(t, axis=1)
acc = 0.0
for i in range(int(x.shape[0] / batch_size)):
tx = x[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]
tt = t[i*batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size]
y = self.predict(tx)
y = np.argmax(y, axis=1)
acc += np.sum(y == tt)
return acc / x.shape[0]
def numerical_gradient(self, x, t):
"""求梯度(数值微分)
Parameters
----------
x : 输入数据
t : 教师标签
Returns
-------
具有各层的梯度的字典变量
grads['W1']、grads['W2']、...是各层的权重
grads['b1']、grads['b2']、...是各层的偏置
"""
loss_w = lambda w: self.loss(x, t)
grads = {}
for idx in (1, 2, 3):
grads['W' + str(idx)] = numerical_gradient(loss_w, self.params['W' + str(idx)])
grads['b' + str(idx)] = numerical_gradient(loss_w, self.params['b' + str(idx)])
return grads
def gradient(self, x, t):
"""求梯度(误差反向传播法)
Parameters
----------
x : 输入数据
t : 教师标签
Returns
-------
具有各层的梯度的字典变量
grads['W1']、grads['W2']、...是各层的权重
grads['b1']、grads['b2']、...是各层的偏置
"""
# forward
self.loss(x, t)
# backward
dout = 1
dout = self.last_layer.backward(dout)
layers = list(self.layers.values())
layers.reverse()
for layer in layers:
dout = layer.backward(dout)
# 设定
grads = {}
grads['W1'], grads['b1'] = self.layers['Conv1'].dW, self.layers['Conv1'].db
grads['W2'], grads['b2'] = self.layers['Affine1'].dW, self.layers['Affine1'].db
grads['W3'], grads['b3'] = self.layers['Affine2'].dW, self.layers['Affine2'].db
return grads
def save_params(self, file_name="params.pkl"):
params = {}
for key, val in self.params.items():
params[key] = val
with open(file_name, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(params, f)
def load_params(self, file_name="params.pkl"):
with open(file_name, 'rb') as f:
params = pickle.load(f)
for key, val in params.items():
self.params[key] = val
for i, key in enumerate(['Conv1', 'Affine1', 'Affine2']):
self.layers[key].W = self.params['W' + str(i+1)]
self.layers[key].b = self.params['b' + str(i+1)]
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 读入数据
(x_train, t_train), (x_test, t_test) = load_mnist(flatten=False)
# 处理花费时间较长的情况下减少数据
x_train, t_train = x_train[:2000], t_train[:2000]
x_test, t_test = x_test[:1000], t_test[:1000]
max_epochs = 20
network = SimpleConvNet(input_dim=(1,28,28),
conv_param = {'filter_num': 30, 'filter_size': 5, 'pad': 0, 'stride': 1},
hidden_size=100, output_size=10, weight_init_std=0.01)
trainer = Trainer(network, x_train, t_train, x_test, t_test,
epochs=max_epochs, mini_batch_size=100,
optimizer='Adam', optimizer_param={'lr': 0.001},
evaluate_sample_num_per_epoch=1000)
trainer.train()
# 保存参数
network.save_params("params.pkl")
print("Saved Network Parameters!")
# 绘制图形
markers = {'train': 'o', 'test': 's'}
x = np.arange(max_epochs)
plt.plot(x, trainer.train_acc_list, marker='o', label='train', markevery=2)
plt.plot(x, trainer.test_acc_list, marker='s', label='test', markevery=2)
plt.xlabel("epochs")
plt.ylabel("accuracy")
plt.ylim(0, 1.0)
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()
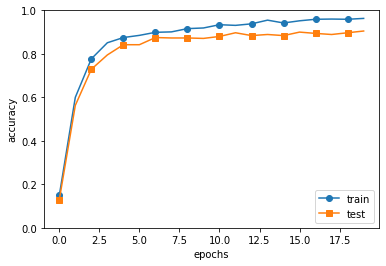
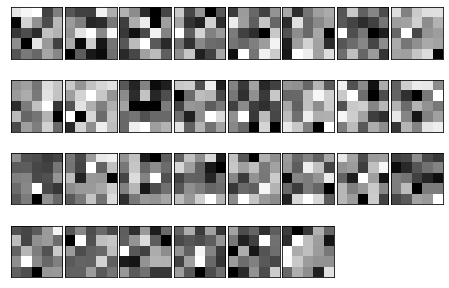
我们可以对比一下训练前与训练后的卷积核的图像,可以发现,训练后,卷积核有了很强的“方向性”,白色部分大多是打横或打竖的。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def filter_show(filters, nx=8, margin=3, scale=10):
"""
c.f. https://gist.github.com/aidiary/07d530d5e08011832b12#file-draw_weight-py
"""
FN, C, FH, FW = filters.shape
ny = int(np.ceil(FN / nx))
fig = plt.figure()
fig.subplots_adjust(left=0, right=1, bottom=0, top=1, hspace=0.05, wspace=0.05)
for i in range(FN):
ax = fig.add_subplot(ny, nx, i+1, xticks=[], yticks=[])
ax.imshow(filters[i, 0], cmap=plt.cm.gray_r, interpolation='nearest')
plt.show()
network = SimpleConvNet()
# 随机进行初始化后的权重
filter_show(network.params['W1'])
# 学习后的权重
network.load_params("params.pkl")
filter_show(network.params['W1'])